New Environment Class 03
BRIEF DISCUSSION OF THE PREVIOUS CLASS (5:12 P.M.)
FUNCTIONS IN ECOSYSTEM (5:24 P.M.)
- Biotic interaction
- Types of Organisms in Ecosystem
- (a) Producers
- These are capable of photosynthesis.
- For example, plants and phytoplankton.
- (b) Herbivores
- These are plant-eating organisms.
- For example, Cow, goat, etc.
- (c) Carnivores
- They feed on herbivores.
- For example, lion, wolf, etc.
- (d) Detrivores/Scavengers
- They feed on dead matter.
- For example, Hyena, Vultures, etc.
- (e) Nectarivores
- They feed on nectar.
- For example, Hummingbird, Sunbird, etc.
- (f) Frugivores
- They eat fruits.
- For example, Parrots, Parakeets, Great Hornbill, Monkeys, etc.
- (g) Gramivores
- They feed mainly on grass.
- For example, Sparrow, Munia, Bluethroat birds, Deers, Horses, Cows, Elephant, Rhinoceros, Indian Bison, etc.
- Types of Organisms Based on Roles
- (a) Flagship species
- Species selected to act as an ambassador, icon, or symbol for the defined habitat, issue, or campaign.
- They are relatively large and charismatic.
- For example, the Tiger, the Great Indian Bustard (Heaviest Flying Bird), etc.
- (*Note: Sarus Crane is the tallest flying bird.)
- (b) Keystone Species
- It is a species that plays an essential role in the functioning or structure of the ecosystem. Its disappearance may cause significant change.
- They have a disproportionately large impact on the ecosystem, compared to their abundance.
- For example, Wolves in Yellowstone National Park (Yellowstone National Park is the first national park in the world.), Honey Bees, Top Predators, Elephants, etc.
- Elephants are called ecosystem engineers.
- (c) Indicator Species
- They indicate certain processes in the ecosystem.
- They are used to assess the environmental condition or the quality of an ecosystem.
- For example, Lichens indicate air pollution, River Dolphins indicate water pollution, Corals indicate sedimentation, Blackbucks indicate the health of grassland, Himalayan Monal indicates the health of the Himalayan ecosystem, etc.
- (d) Umbrella Species
- These are the dominant species in the ecosystem and are representatives of that ecosystem.
- By protecting the umbrella species, all other species can be easily protected.
- For example, Corals, Kelps, and top predators.
- Ecosystem Services (6:05 P.M.)
- four types of services are provided by the ecosystem:
- (a) Provisioning Services
- The "products" are obtained from the ecosystem.
- For example, Foods, Fibers, Ornamentals, Minerals, etc.
- (b) Regulating Services
- The benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes.
- For example, Climate Regulation, Flood Prevention, etc.
- (c) Cultural Services
- These refer to the non-material services obtained from the ecosystem.
- For example, Educational, recreational, etc.
- (d) Supporting Services
- These services are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services.
- For example, Biodiversity, Nutrient Cycle, etc.
BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES (6:11 P.M.)
- The flow of different chemical elements and compounds between different organisms and the physical environment is called as Biogeochemical Cycle.
- These are classified into the gaseous cycles and sedimentary cycles.
- (a) Gaseous Cycle
- In this, the reservoir pool is the atmosphere.
- For example, Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, Water Cycle, and Oxygen Cycle.
- (b) Sedimentary Cycle
- The reservoir pool is in the Earth's crust or lithosphere.
- For example, the Sulphur Cycle and Phosphorous Cycle.
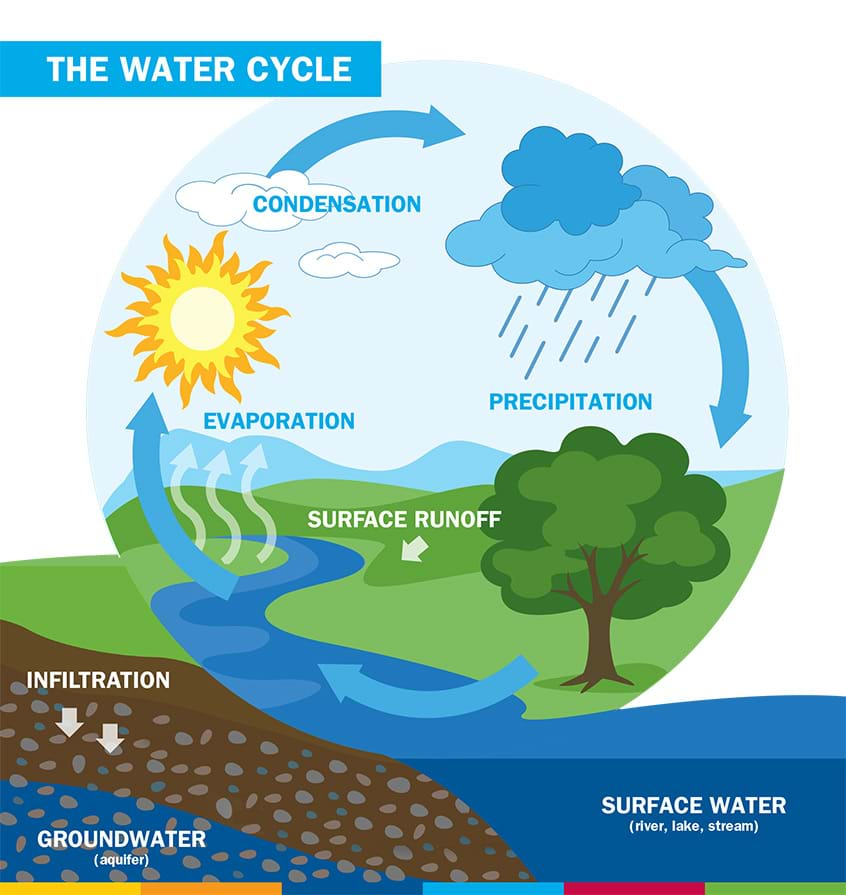
WATER CYCLE (6:21 P.M.)
- The water vapour converts into water through the process of condensation.
- This water accumulates around the hygroscopic particles, leading to cloud formation.
- The precipitation would lead to the falling of the water on the surface.
- When water vapour condenses on the ground, it may result in different condensation forms like fog, mist, dew, and frost.
- The water converts into water vapour by absorbing the heat. This process is called evaporation.
-
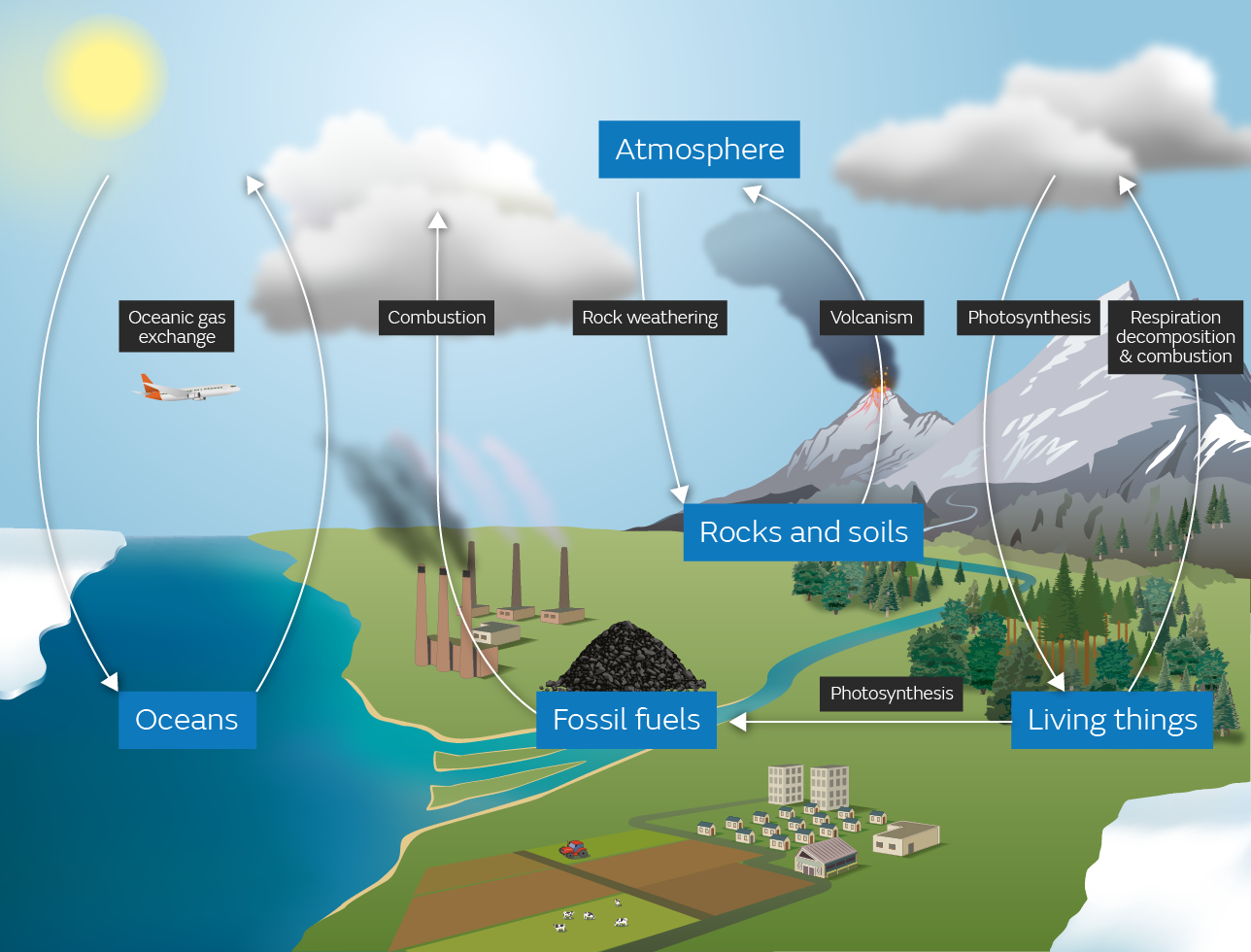
CARBON CYCLE (6:30 P.M.)
- The carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere enters the plants through the process of photosynthesis.
- The equation of photosynthesis is 6CO2+ 6H2O+ Sunlight -> C6H12O6+ 6O2.
- The plants store it in the form of carbohydrates.
- The consumers consume the plants, there by it goes into the consumers.
- The consumers give out carbon dioxide by the process of respiration.
- The plants also perform the respiration to release the carbon dioxide.
- Plants and consumers after their death convert into the soil organic matter.
- This soil organic matter decomposes to release the carbon into the atmosphere.
- Some soil organic matter will convert into fossil fuel.
- This fossil fuel on combustion will release the carbon into the atmosphere.
- The oceans are capable of absorbing the carbon dioxide. They release it back, once they get saturated.
-
OXYGEN CYCLE
- Plants convert the atmospheric carbon dioxide into the atmospheric oxygen.
- This is taken by the plants and animals which convert it into carbon dioxide (Respiration Process).
- Also, the oxides release the oxygen into the atmosphere.
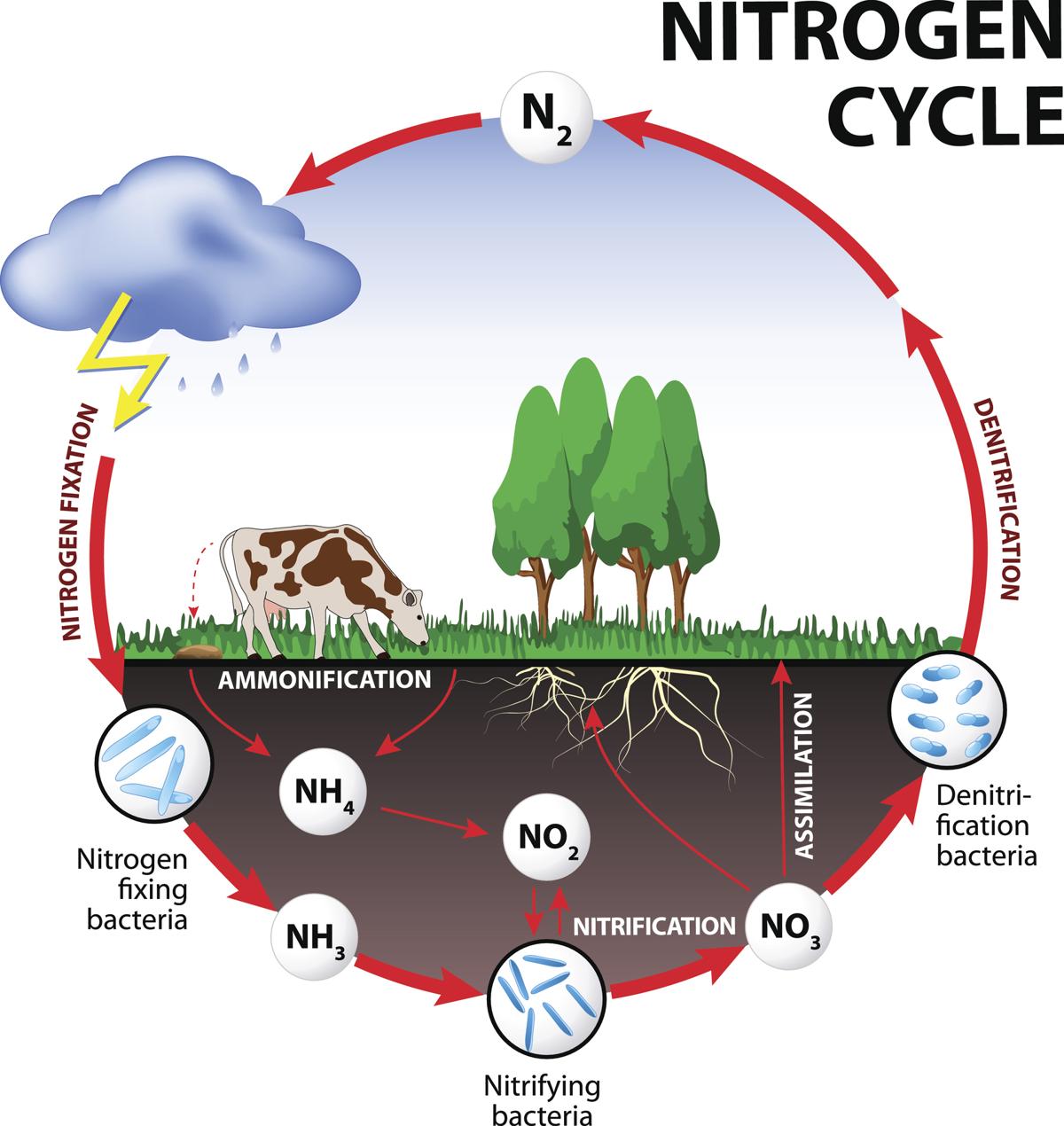
NITROGEN CYCLE (7:06 P.M.)
- Nitrogen is present abundantly in the atmosphere.
- The conversion of nitrogen into ammonia is called Nitrogen Fixation.
- Nitrogen Fixation is carried out by free-living bacteria in the soil. For example, Azatobacter and Clostridium.
- Nitrogen Fixation is carried out by the symbiotic microbes as well. For example, Rhizobium and Blue Green Algae (Anabena and Spirulena).
- Nitrogen Fixation happens naturally during the lightening as well.
- It can be carried out by industrial processes as well.
- Ammonia is converted into Nitrite and Nitrate through the process of Nitrification.
- Nitrosomonas converts the ammonia into nitrites.
- Nitrobacter converts the nitrite into nitrates.
- The nitrate is converted into ammonia through the process of Ammonification.
- Nitrate is converted into nitrogen through the process of Denitrification.
- Pseudomonas converts the nitrites and nitrates into the nitrogen.
-
- Fossil fuels also contain some nitrogen compounds. On combustion, the oxides of the nitrogen reach the atmosphere.
- This further comes down with rain in the form of nitric acid.
PHOSPHOROUS CYCLE (7:28 P.M.)
- The phosphorous is stored in the rocks.
- The phosphorous is released into the soil through the processes of weathering, erosion, etc.
- In the soil, the phosphorous is present in the form of phosphates.
- The plants take this phosphate through the process of assimilation.
- Through consumption, it travels higher in the food cycle.
- From the consumers, it reaches the soil through the process of excretion and decomposition.
- Rain, rivers, and other such agents take away the phosphorous from the soil and deposit it into the basin.
- Through the process of lithification, it again gets stored in the rocks.
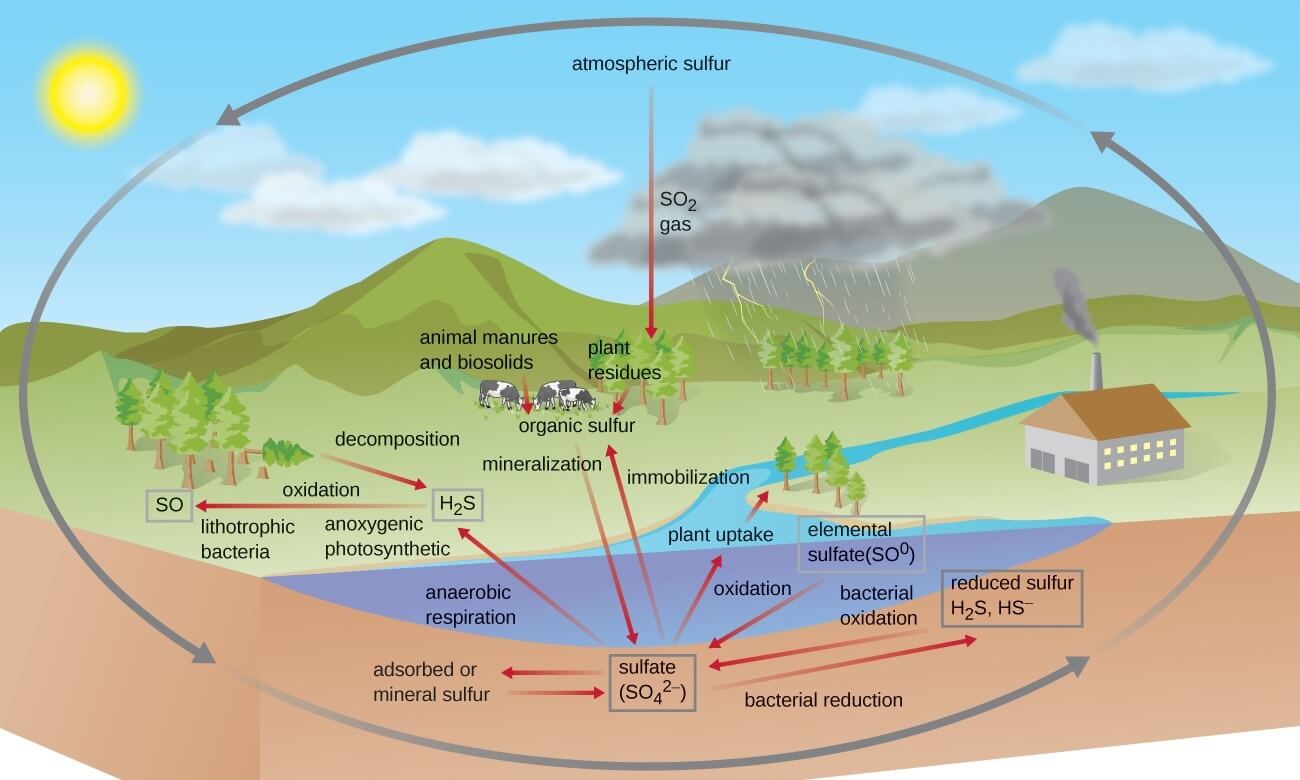
SULPHUR CYCLE
- There is an interaction with the atmosphere, but the reservoir is in the lithosphere.
- It is stored in the form of organic and inorganic forms.
- In the organic form, it is stored in the form of coal, petroleum, and peat.
- In the inorganic form, it is stored in the form of sulfates and sulfides.
-
TIGERS (7:40 P.M.)
- The various statuses are Not Evaluated, Data Insufficient, Least Concern, Near Threatened, Vulnerable, Endangered, Critically Endangered, Extinct in Wild, and Extinct.
- Big cats in India are Lion, Tiger, Cheetah, Snow Leopard, and Leopard.
- Jaguar and Puma are not present in India.
- The IUCN status of the tiger is endangered.
- Tiger is in Appendix 1 of the CITES.
- There are several subspecies of tiger,
- It is present in 13 countries, where it is found in the wild. These countries are called Tiger-Range countries.
- India, Nepal, Bangladesh, Bhutan, Myanmar, Thailand, Laos, Vietnam, Cambodia, Malaysia, Indonesia, China, and Russia are such countries.
- India hosts 70% of the world's tigers.
- The various subspecies of tigers can be classified into continental tigers and Island tigers.
- The Royal Bengal Tiger is a continental tiger.
- The Indo-China Tiger is also a continental tiger.
- The Malayan Tiger is a continental tiger.
- Sumatran and Javan tigers are island tigers.
- The Bali Tiger is extinct.
- China has a South-China tiger, which is a continental tiger.
- The Amur/Siberian tiger is found in Siberia. It is the biggest species of tiger.
- The tiger is the largest of all the big cats.
- The tiger is very important as it is a keystone, flagship, and umbrella species.
THE TOPIC FOR THE NEXT CLASS: DIFFERENT TYPES OF ECOSYSTEMS, BIOMES, AND WETLANDS.